Recently, the research group of Professor Guo Yanbing of the School of Chemistry has made important progress in removing heavy metal lead ions from alkyne rich Graphyne based materials, The research findings titled "Ultra high efficiency capture of lead ions over acetylenic bond rich graphdyne adsorbent in acute solution" (PNAS, 2023120, 16) were published in the authoritative international scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS). Xie Shuanglei, a 2019 joint postgraduate of Wuhan Institute of Technology, and Pan Chuanqi, a 2019 doctoral candidate of our university, are the co first authors of the paper. The corresponding authors are Mao Xuefei, a researcher of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Li Junbo, a professor of Wuhan Institute of Technology, and Guo Yanbing, a professor of our university (the last corresponding author). The first completion unit is Central China Normal University.
Lead (Pb) is a Toxic heavy metal, which can enter the blood and bones through various exposure routes, such as food, water, air, tobacco and automobile exhaust. According to reports, at least 9 million tons of lead have been released into the global environment, with a significant portion entering water resources and gradually entering the biological chain through certain media. Lead is not degradable in organisms and can accumulate within them. Long term systemic exposure to lead may lead to hypertension, heart disease, stroke, and chronic kidney disease. More noteworthy is that even if the lead content in the blood of pregnant women is below 10 μ G/L may also lead to issues such as miscarriage, premature birth, low birth weight, and delayed development in children. Therefore, effectively removing lead from liquid media is of great significance for protecting environmental safety and human health.
In recent years, with funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Hubei Provincial Outstanding Youth Fund, Guo Yanbing's research group has conducted in-depth exploration on the application of acetylene bond regulated interface electronic structure in the field of environmental remediation. The concept of "sp-carbon mediated oxygen activation" was first proposed internationally and systematic research was first conducted.
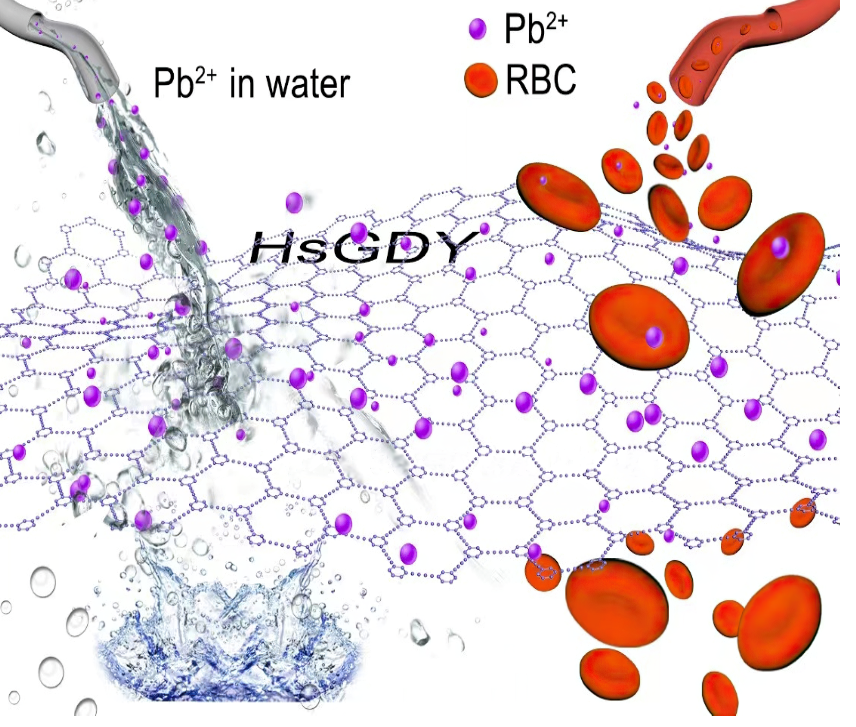
Schematic diagram of removal of lead in aqueous solution and blood by hydrogenated Graphyne
In this work, Professor Guo Yanbing's team, together with Professor Li Junbo of Wuhan Institute of Technology and researcher Mao Xuefei of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, built hydrogenated Graphyne (HsGDY) with unique alkyne bond and large hexagonal pore structure, and used it for the first time to capture lead ions in water phase and lead containing blood. Research has found that the unique hexagonal pore structure and stacking mode of HsGDY allow it to adsorb more lead through the in-plane edge adsorption configuration per unit space. The hybridization of Pb 6s and H 1s orbitals promotes strong bonding of lead atoms adsorbed on the acetylene bond of HsGDY, which helps to improve the adsorption capacity of HsGDY. Based on the above structural advantages, HsGDY exhibits extremely high absorption of lead