第一作者:方亚蓉,李慧娟
通讯作者:罗竹副教授、郭彦炳教授
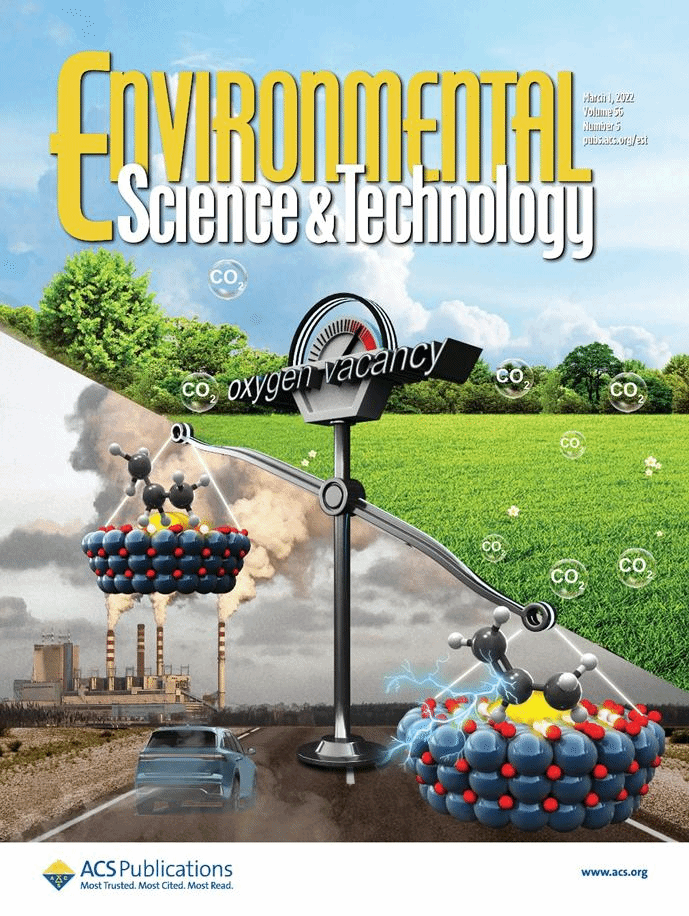
论文DOI:10.1021/acs.est.1c07573
图文摘要
成果简介
近日,华中师范大学郭彦炳教授课题组在Environmental Science & Technology上发表了题为“Oxygen Vacancy Governed Opposite Catalytic Performance for C3H6 and C3H8 Combustion: The Effect of Pt Electronic Structure and Chemisorbed Oxygen Species”的研究论文(DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.1c07573),分别探究了Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面氧空位对丙烯(C3H6)、丙烷(C3H8)催化燃烧的不同机制。该文通过氧空位调控策略合成了富含氧空位的Pt/TiO2-x催化剂,研究了氧空位对Pt电子结构的改变以及对表面化学吸附氧物种的影响,深入揭示了氧空位对催化氧化短链不饱和烃C3H6的促进作用和短链饱和烃丙烷C3H8的抑制作用。该研究为合成高效率、高稳定性的Pt基催化剂及其环境催化应用提供了理论指导。
引言
以丙烯(C3H6)、丙烷(C3H8)为代表的直链烃类是大气污染物VOCs的主要构成之一,其环境危害不容小觑。贵金属Pt是工业上常用的VOCs催化氧化催化剂,构建表面氧空位是提高催化氧化性能的常用策略。然而,在催化氧化反应过程中,氧空位对具有不同分子结构的短链不饱和烃C3H6和短链饱和烃C3H8的作用机制尚不明确。因此,本工作研究了富含表面氧空位的Pt/TiO2-x催化剂的C3H6、C3H8催化氧化性能;结合理论计算和光谱学表征,研究了表面氧空位对Pt纳米颗粒的粒径大小、表面价态等性质的影响;探究了表面氧空位对O2的吸附位点、吸附能和活化能的影响;揭示了上述性质对C3H6和C3H8催化氧化的不同作用机制。
图文导读
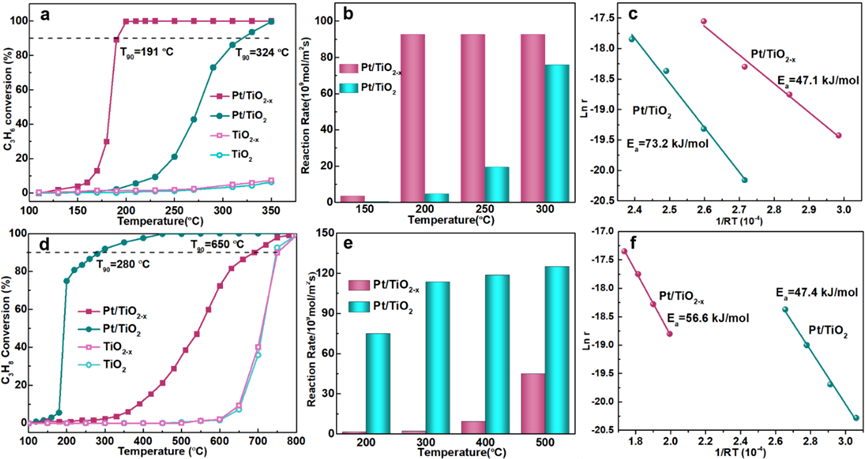
样品结构
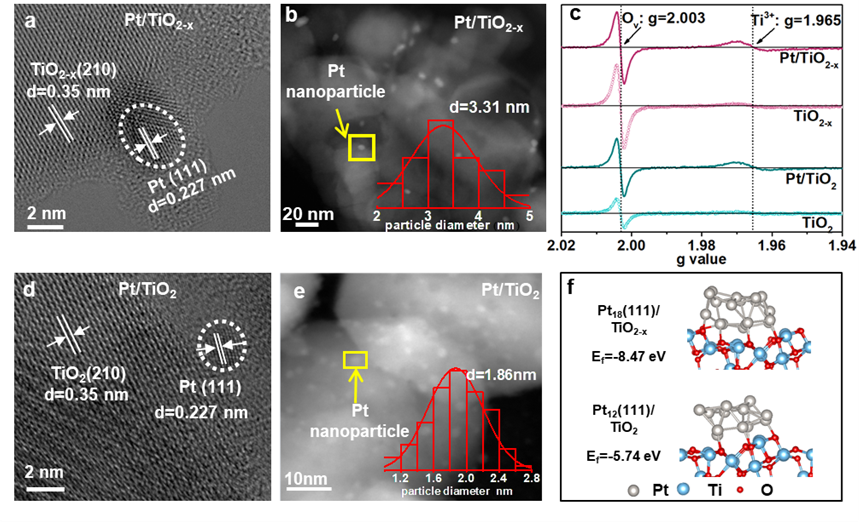
Figure 2. High resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) images of a: Pt/TiO2-x;d: Pt/TiO2 catalysts; The high-angle annular dark-field scanning (HAADF) image of b: Pt/TiO2-x;e: Pt/TiO2; The insertion shows the corresponding size distribution of platinum nanoparticles; c: Low-temperature (liquid nitrogen, -196 °C) electron paramagnet icresonance (EPR) spectra collected in vacuum; f: The simulated Pt18(111)/TiO2-x and Pt12(111)/TiO2 models and corresponding calculated formation energy.
HRTEM结果表明,相较于Pt/TiO2催化剂,导致Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面负载的Pt纳米颗粒尺寸较大(3.31 nm vs. 1.86 nm)。EPR和DFT结果表明,TiO2载体的表面氧空位可以作为Pt纳米颗粒生长的成核中心并促进Pt纳米颗粒的生长。
表面吸附氧物种
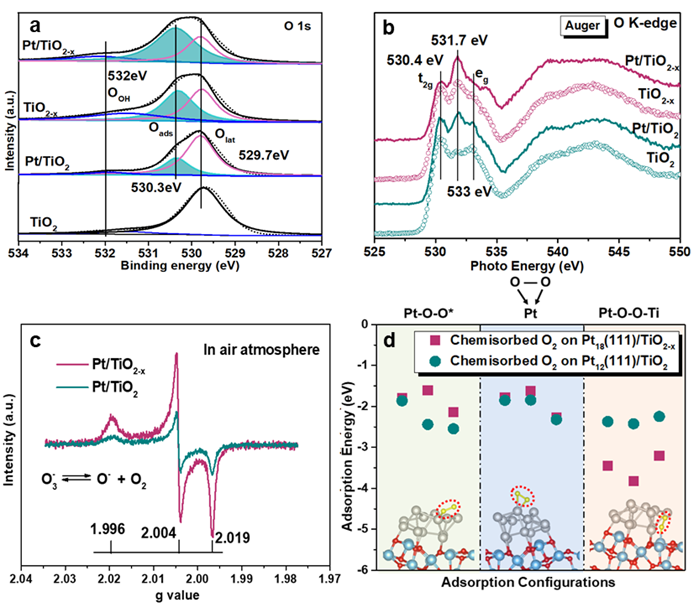
Figure 3. a: O 1sXPS spectra of TiO2, TiO2-x, Pt/TiO2 and Pt/TiO2-x catalysts; b: O k-edge XANES spectra of Pt/TiO2 and Pt/TiO2-x catalysts; c: Room-Temperature electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra collected in air atmosphere; d: Three typical O2 adsorption configurations on Pt18(111)/TiO2-x surface and Pt12(111)/TiO2 surface, and corresponding oxygen molecule adsorption energies.
结合O 1s XPS图谱和O K-边 XANES图谱,我们发现富含氧空位的Pt/TiO2-x催化剂中Pt纳米颗粒与TiO2-x载体界面处存在丰富的吸附氧物种,DFT结果表明该吸附氧物种的吸附构型为Pt-O-O-Ti,表现出过氧化物种(O22-)的结构性质,具有很好的稳定性。
Pt的电子结构
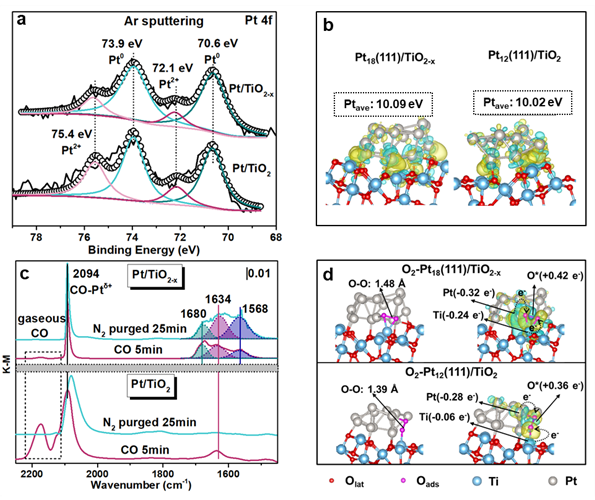
Figure 4. a: Pt 4f X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) of Pt/TiO2 and Pt/TiO2-x catalysts after Ar sputter; b: the 3D isosurface of local charge density difference (down) of Pt18(111)/TiO2-x and Pt12(111)/TiO2 models; electron accumulation and depletion are represented by yellow and cyan respectively. c: CO adsorption DRIFTS spectra over Pt/TiO2-x and Pt/TiO2 catalysts, respectively. d: the pristine configuration (up) and 3D isosurface of local charge density difference (down) of O2 adsorbed Pt18(111)/TiO2-x and O2 adsorbed Pt12(111)/TiO2 models; electron accumulation and depletion are represented by yellow and cyan.
Pt 4f XPS图谱和DFT结果表明,富氧空位Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面负载的Pt纳米颗粒与氧空位之间存在电荷转移,氧空位限域的电子转移至Pt位点,促进了还原态Pt0物种的生成。
Pt0促进的C3H6催化氧化
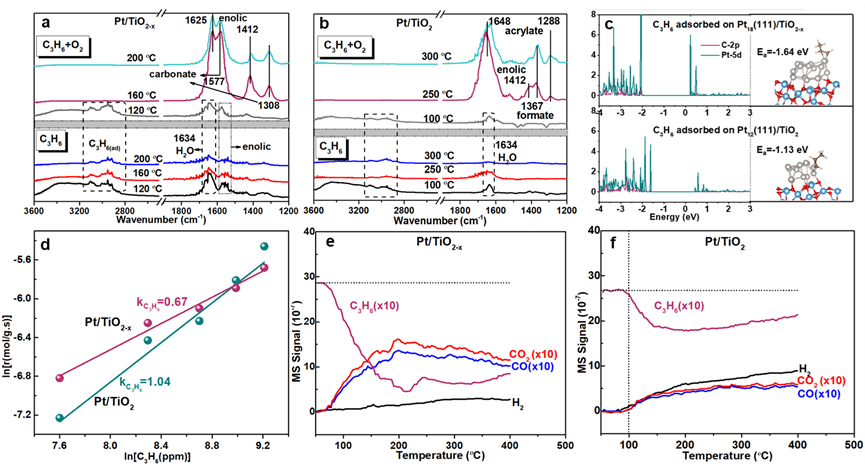
Figure 5. In situ DRIFTS spectra of propene adsorption under pure C3H6 stream (down) and propene oxidation under C3H6+O2 stream (upper) on a: Pt/TiO2-x catalyst and b: Pt/TiO2;c: Left: Projected density of states (PDOS) plots of Pt d orbitals (blue) and adsorbed carbon (in C3H6 molecule) 2p orbitals (purple) on Pt18(111)/TiO2-x(upper) and Pt12(111)/TiO2 (down) surface; Right: the typical C3H6 adsorption configurations and corresponding adsorption energy (Ea); d: Dependence of reaction rate onpartial pressure of O2 of Pt/TiO2-x and Pt/TiO2 catalysts. The outlet gas components of e: Pt/TiO2-x and f: Pt/TiO2 catalysts during C3H6 temperature programmed surface reaction (C3H6-TPSR) experiments.
C3H6-DRIFTS和DFT结果表明,Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面的活性还原态Pt0位点可通过有效活化C=C键从而促进了C3H6分子的化学吸附、活化,促进中间产物羧酸盐和碳酸盐的生成及其进一步的完全氧化为CO2。
界面吸附Pt-O-O-Ti抑制的C3H8催化氧化
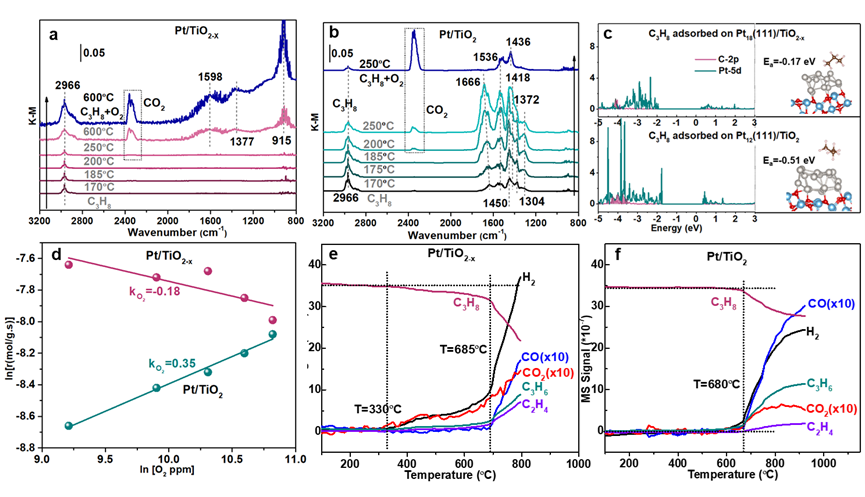
Figure 6. In situ DRIFTS spectra on a: Pt/TiO2-x catalyst and b: Pt/TiO2 during propane adsorption and propane oxidation; c: Left: projected density of states (PDOS) plots of Pt d orbitals (blue) and adsorbed carbon (in C3H8 molecule) 2p orbitals (purple) on Pt18(111)/TiO2-x (upper) and Pt12(111)/TiO2 (down) surface; Right: the typical C3H8 adsorption configurations and corresponding adsorption energy (Ea); d: Dependence of reaction rate on partial pressure of O2 of Pt/TiO2-x and Pt/TiO2 catalysts. The outlet gas components of e: Pt/TiO2-x and f: Pt/TiO2 catalysts during C3H8 temperature programmed surface reaction (C3H8-TPSR) experiments.
C3H8-DRIFTS和DFT结果表明,氧空位促进了O2以Pt-O-O-Ti物种的形式被吸附,而O2和C3H8分子之间的竞争吸附严重抑制了C3H8分子的有效吸附,进而抑制了丙烷的催化燃烧。
小结
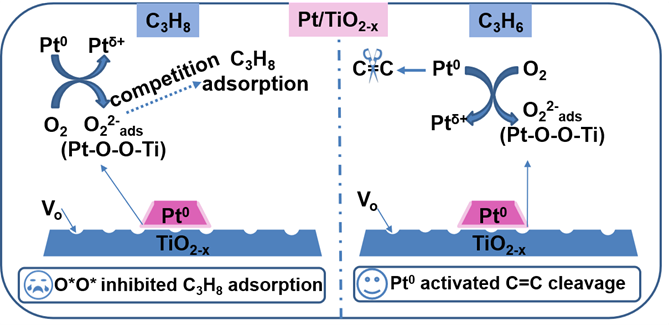
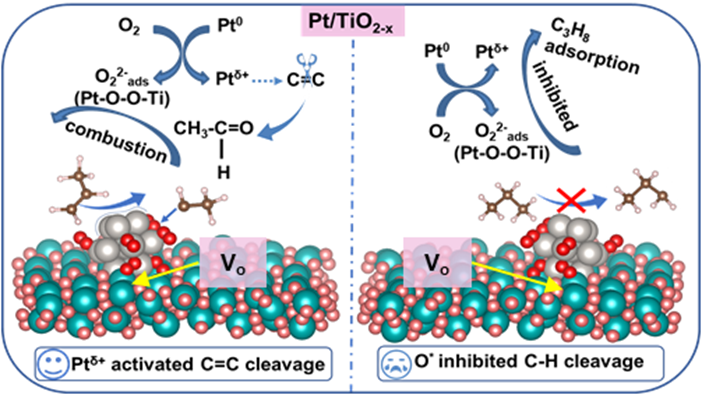
Scheme 1. The catalytic mechanism of the promotion of C3H6 combustion (left) and suppression of C3H8 combustion (right) over the surface of Pt/TiO2-x catalyst.
该工作通过氧空位调控策略合成了富氧空位的Pt/TiO2-x催化剂,并进一步研究了氧空位对Pt电子特性和化学吸附氧物种的影响,深入揭示了C3H6和C3H8不同的催化燃烧机制。Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面氧空位和负载的Pt纳米颗粒之间存在电荷转移,并导致大量还原性Pt0物种以及化学吸附的过氧物种O22-(Pt-O-O-Ti)的产生。还原性Pt0物种可作为丙烯分子的吸附、活化位点,有效促进C=C双键的断裂,显著提高C3H6催化氧化效率。相反,Pt/TiO2-x催化剂表面由于O2和C3H8分子之间的竞争吸附抑制了C3H8分子的物理吸附以及活化,从而降低了C3H8催化燃烧效率。该研究清晰地阐明了催化剂表面氧空位与短链直链烃类催化氧化的构效关系,为设计高效VOCs催化氧化催化剂提供了理论指导。
作者介绍

郭彦炳 博士,教授,博士生导师,现任职于华中师范大学化学学院,副院长。国家青千、湖北省百人计划创新人才,中国化学会青委会委员,Chinese Chemical Letter期刊青年编委。曾先后在美国康涅狄格大学、麻省理工学院(MIT)和美国三维阵列科技有限公司从事高效催化剂制备及汽车尾气后处理系统研发。目前主要从事高稳定性气相污染物净化催化剂创制领域的研究,主持国家级青年人才启动基金、国家自然科学基金面上项目等10余个。累计发表SCI论文70多篇,以通讯和第一作者在Nature Commun., J. Am. Chem. Soc., Adv. Mater., Environ. Sci. Tech.等一区论文20多篇,引用3000余次,H因子27。

罗竹 博士,副教授,硕士生导师,现任职于华中师范大学化学学院。2016年毕业于美国康涅狄格大学,入选湖北省楚天学者计划。目前主要研究领域为纳米材料的改性及其在气相环境催化反应中的应用。在J. Am. Chem. Soc., Adv. Energy Mater., Chem. Mater., Angew. Chem.等学术期刊发表论文30余篇,被引用1200余次,H因子 19,获批美国专利1项,国内专利1项。
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.1c07573
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/IrejQDA5CEn6Y6BwplRWiw