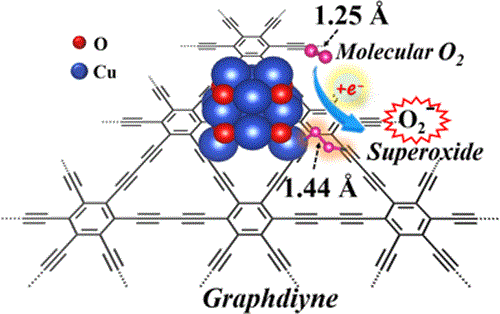
Activation of O2is a crucial step in oxidation processes. Here, the conceptof sp-hybridized C & xe0c9;C triple bonds as an electron donor is adopted to develop highlyactive and stable catalysts for molecular oxygen activation. We demonstrate that theneighboring sp-hybridized C and Cu sites on the interface of the sub-nanocluster CuO/graphdiyne are the key structures to effectively modulate the O2activation process in thebridging adsorption mode. The as-prepared sub-nanocluster CuO/graphdiyne catalystexhibited the highest CO oxidation activity and readily converted 50% CO at around 133 degrees C, which is 34 and 94 degrees C lower than that for CuO/graphene and CuO/active carboncatalysts, respectively. In situ diffused reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopyand density functional theory calculation results proved that the neighboring sp-hybridizedC is more favorable to promote the rapid dissociation of carbonate than sp2-hybridized C without overcoming any energy barrier.The gaseous CO directly reacts with the active molecular oxygen and tends to proceed through the E-R mechanism with a relativelylow energy barrier (0.20 eV). This work revealed that sp-hybridized C of graphdiyne-based materials could effectively improve theO2activation efficiency, which could facilitate the low-temperature oxidation processes.